Phoenix Data Sources
Page edited by Steven Hawkins
Changes (2)
| ... |
| {info} |
| Phoenix Connection AutoCommit default is false, set _phoenix.connection.autoCommit_ property to true is necessary if execute INSERT/UPDATE/DELETE. |
| The Phoenix Connection AutoCommit default is false. Set _phoenix.connection.autoCommit_ to true if you will be executing INSERT/UPDATE/DELETE statements against Phoenix. |
| |
| ... |
Full Content
Phoenix Data Sources
The following is a example for setting up Phoenix Data Sources, which is precondition for Apache HBase Translator. In addition to the Data Sources set up, this article also cover mapping Phoenix table to an existing HBase table and creating a new Phoenix table.
There are configuration templates for Phoenix data sources in the "<jboss-install>/docs/teiid/datasources" directory. A complete description how a data source can be added into JBoss AS7.x is also described here.
Configuring a Phoenix data source in JBoss/WildFly (JBoss AS 7.x or later)
Configuring a Phoenix data source is nearly identical to configuring JDBC Data Sources. The first step is deploying the Phoenix driver jar. Using below CLI command to deploy Phoenix driver:
module add --name=org.apache.phoenix --resources=/path/to/phoenix-[version]-client.jar --dependencies=javax.api,sun.jdk,org.apache.log4j,javax.transaction.api /subsystem=datasources/jdbc-driver=phoenix:add(driver-name=phoenix,driver-module-name=org.apache.phoenix,driver-class-name=org.apache.phoenix.jdbc.PhoenixDriver)
The Driver jar can be download from phoenix document.
The second steps is creating the Data Source base on above deployed driver, which is also like creating JDBC Data Source. Using below CLI command to create Data Source:
/subsystem=datasources/data-source=phoenixDS:add(jndi-name=java:/phoenixDS, driver-name=phoenix, connection-url=jdbc:phoenix:{zookeeper quorum server}, enabled=true, use-java-context=true, user-name={user}, password={password})
/subsystem=datasources/data-source=phoenixDS/connection-properties=phoenix.connection.autoCommit:add(value=true)
Please make sure the URL, Driver, and other properties are configured correctly:
- jndi-name - The JNDI name need to match the JNDI name you used in VDB
- driver-name - The Driver name need to match the driver you deployed in above steps
- connection-url - The URL need to match the HBase zookeeper quorum server, the format like jdbc:phoenix [ :<zookeeper quorum> [ :<port number> ] [ :<root node> ] ], 'jdbc:phoenix:127.0.0.1:2181' is a example
- user-name/password - The user credentials for Phoenix Connection
| The Phoenix Connection AutoCommit default is false. Set phoenix.connection.autoCommit to true if you will be executing INSERT/UPDATE/DELETE statements against Phoenix. |
Mapping Phoenix table to an existing HBase table
Mapping Phoenix table to an existing HBase table has 2 steps. The first step is installing phoenix-[version]-server.jar to the classpath of every HBase region server. An easy way to do this is to copy it into the HBase lib - for more details please refer to the phoenix documentation.
The second step is executing the DDL to map a Phoenix table to an existing HBase table. The DDL can either be executed via Phoenix Command Line, or executed by JDBC.
The Following is a example for mapping an existing HBase Customer with the following structure:
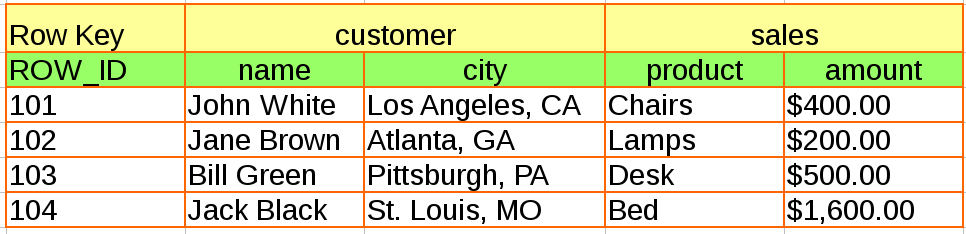
As depicted above, the HBase Customer table have 2 column families, customer and sales, and each has 2 column qualifiers, name, city, product and amount respectively. We can map this Table to Phoenix via DDL:
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS "Customer"("ROW_ID" VARCHAR PRIMARY KEY, "customer"."city" VARCHAR, "customer"."name" VARCHAR, "sales"."amount" VARCHAR, "sales"."product" VARCHAR)
For more about mapping Phoenix table to an existing HBase table please refer to the phoenix documentation.
Creating a new Phoenix table
Creating a new Phoenix table is just like mapping to an existing HBase table. Phoenix will create any metadata (table, column families) that do not exist. Similar to the above example the DDL to create the Phoenix/HBase Customer table would be:
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS "Customer"("ROW_ID" VARCHAR PRIMARY KEY, "customer"."city" VARCHAR, "customer"."name" VARCHAR, "sales"."amount" VARCHAR, "sales"."product" VARCHAR)